5 Key Differences Between SSDs and HDDs and Why They Matter
You go to a computer shop to buy a laptop. The shopkeeper asks you what internal storage device you need in your laptop. Should it be SSD or HDD but you are not in a position to answer him since you don’t know the difference between them. Well, we’re here to address this confusion of yours!
You go to a computer shop to buy a laptop. The shopkeeper asks you what internal storage device you need in your laptop. Should it be SSD or HDD but you are not in a position to answer him since you don’t know the difference between them.
Well, we’re here to address this confusion of yours!
Slow PCs not only eat up our time but can also dampen our overall experience and productivity. Imagine investing in a storage device only to find out it's not optimal for your daily tasks.
Frustrating, right? As technology rapidly evolves, making informed decisions is crucial. Not just for performance, but for longevity and value for your hard-earned money.
If you've ever been curious about how to elevate your computer's performance, you're in the right place.
In this blog post, we’ll share 5 differences between SSDs and HDDs. After reading you'll not only understand these differences but will also be able to make informed decisions about your computer's storage.
Core Differences Between SSDs and HDDs
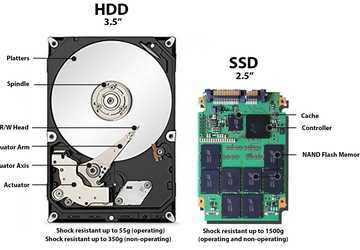
The world of storage devices can seem complex, but it doesn't have to be. The key to faster, more efficient computing may lie in the difference between SSDs and HDDs.
SSDs and HDDs are both crucial for storing your computer's data. While SSDs offer
faster speeds and durability, HDDs provide larger storage at a lower cost.
1. The Mechanism: No Moving Parts vs. Spinning Disks
At the core of SSDs (Solid State Drives) is the fact that they don't have any moving parts. Instead, they rely on NAND-based flash memory.
Key features SSDs:
● Faster data retrieval as there's no physical read/write head to move.
● Reduced risk of physical damage or wear and tear.
● Less noise and heat production.
In contrast, HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) use spinning disks.
Key features of HDDs:
● Slower data access times.
● Potential for mechanical failure.
● Noticeable heat and sound when in use.
Swapping to an SSD means a quieter, cooler, and overall faster computer experience.
2. Cost and Capacity: Price Drops vs. Storage Galore
Historically, SSDs were expensive. However, as technology advances, the price gap between SSDs and HDDs has been narrowing.
Key features SSDs:
● SSD prices have plummeted, making them accessible to many.
● SSDs offer faster speeds even at smaller capacities.
Key features HDDs:
● Provide massive storage options at budget-friendly prices.
● Are still preferred for tasks that require a lot of space but not necessarily speed.
If speed is your game, SSDs are the way to go. But if you're looking for vast storage on a budget, HDDs still hold their ground.
3. Power Consumption: Efficiency vs. Energy Drains
SSDs are known for their energy efficiency. With no moving parts, they consume less power.
Key features SSDs:
● A noticeable increase in battery life for laptops.
● Reduced electricity costs in the long run.
● Lower heat generation, reducing the need for active cooling.
HDDs, with their spinning disks, tend to:
Key features HDDs:
● Draw more power due to mechanical components.
● Result in shorter battery life for portable devices.
● Contribute more to system heat, often requiring better cooling solutions.
If you’re eco-conscious or seeking longer battery life on the go, SSDs hold a clear advantage.
4. Durability and Lifespan: Robustness vs. Wear and Tear

The construction of SSDs offers better durability because:
Key features SSDs:
● Lack of mechanical parts means fewer points of failure.
● They can withstand shocks and bumps better, making them ideal for laptops.
● With advancements in technology, SSD lifespan has increased significantly.
Key features HDDs:
● Are susceptible to mechanical failures.
● Can lose data if dropped or subjected to sudden movements.
● Generally have a fixed lifespan based on read/write limitations.
For those leading an active lifestyle or those prone to accidents, SSDs offer peace of mind with their robustness.
5. Form Factor and Flexibility: Compact vs. Conventional
SSDs offer more flexibility in terms of form factor.
Key features SSDs:
● Come in various sizes, including smaller M.2 or PCIe formats.
● Can be integrated into ultra-thin laptops or even tablets.
● Offer potential for innovative system designs due to compactness.
Key features HDDs:
● Have a more standardized and bulkier form factor.
● Are less adaptable to compact device designs.
● Often requires more space, limiting design innovations.
If sleek designs, ultra-portable devices, or cutting-edge tech appeal to you, SSDs pave the way for such advancements.
The SSD vs. HDD debate is not about declaring one as obsolete and the other as superior. It’s about understanding which fits your specific needs.
If you crave faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and a silent workspace, SSDs are your best friend.
However, if your work revolves around tons of data and you're on a budget, HDDs won't disappoint.
Ready to upgrade or make that informed storage decision? Dive in and witness the transformation in your computing experience!